Patient characteristics
A 35-year-old mother of four presented with recurrence of bilateral refluxing varicosities after previous thermal ablation treatment at another facility. Her symptoms included leg fatigue, heaviness and ankle swelling.
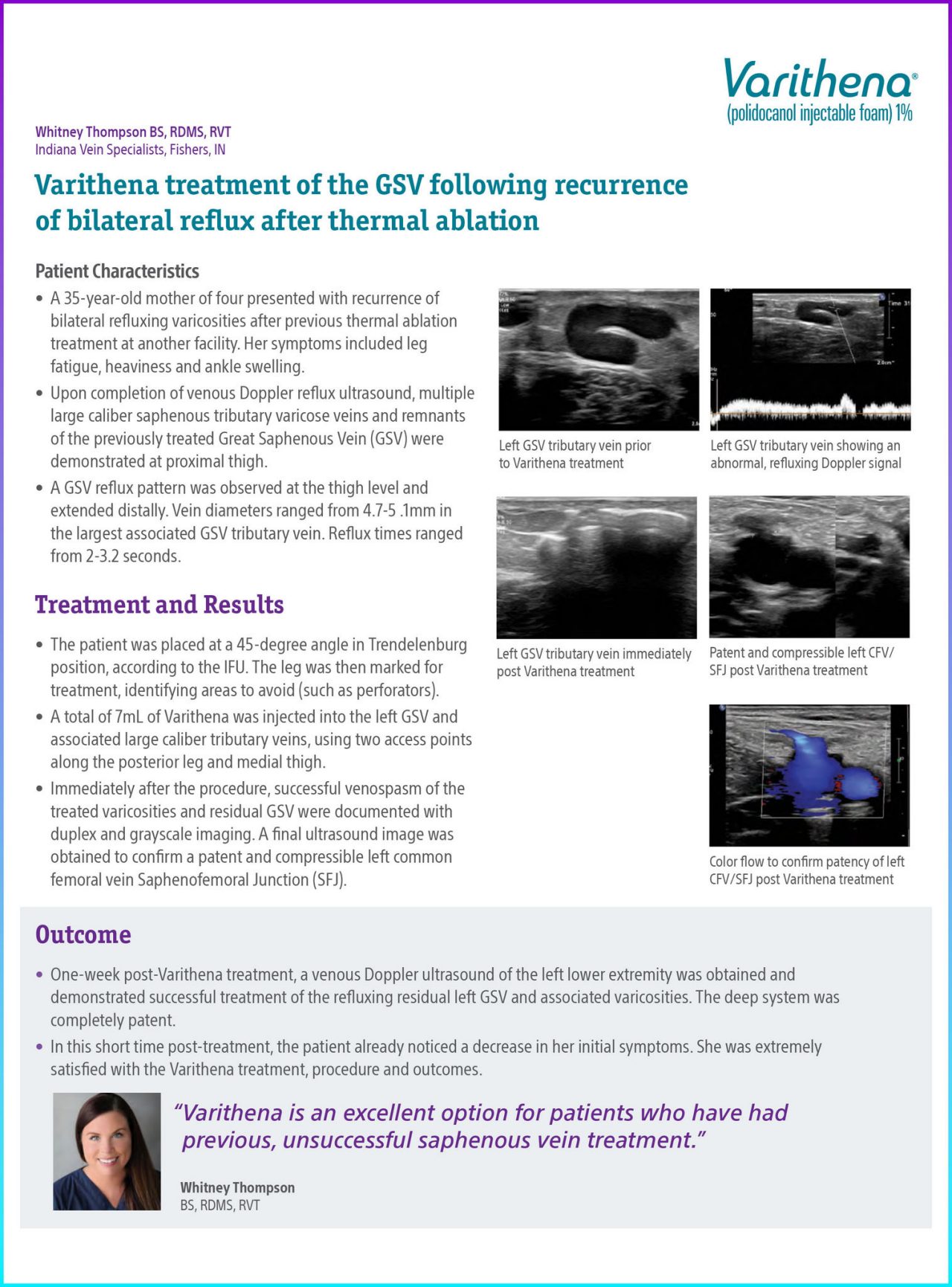
Upon completion of venous Doppler reflux ultrasound, multiple large caliber saphenous tributary varicose veins and remnants of the previously treated Great Saphenous Vein (GSV) were demonstrated at proximal thigh.
A GSV reflux pattern was observed at the thigh level and extended distally. Vein diameters ranged from 4.7-5 .1mm in the largest associated GSV tributary vein. Reflux times ranged from 2-3.2 seconds.
Treatment and results
The patient was placed at a 45-degree angle in Trendelenburg position, according to the IFU. The leg was then marked for treatment, identifying areas to avoid (such as perforators).
A total of 7mL of Varithena was injected into the left GSV and associated large caliber tributary veins, using two access points along the posterior leg and medial thigh.
Immediately after the procedure, successful venospasm of the treated varicosities and residual GSV were documented with duplex and grayscale imaging. A final ultrasound image was obtained to confirm a patent and compressible left common femoral vein Saphenofemoral Junction (SFJ).
Conclusion
One week post-Varithena treatment, a venous Doppler ultrasound of the left lower extremity was obtained and demonstrated successful treatment of the refluxing residual left GSV and associated varicosities. The deep system was completely patent.
In this short time post-treatment, the patient already noticed a decrease in her initial symptoms. She was extremely satisfied with the Varithena treatment, procedure and outcomes.
Documentation

Figure 1. Left GSV tributary vein prior to Varithena treatment.

Figure 2. Left GSV tributary vein showing an abnormal, refluxing Doppler signal.

Figure 3. Left GSV tributary vein immediately post Varithena treatment.

Figure 4. Patent and compressible left CFV/SFJ post Varithena treatment.

Figure 5. Color flow to confirm patency of left CFV/SFJ post Varithena treatment.
* Results from case studies are not necessarily predictive of results in other cases. Results in other cases may vary.