Patient Characteristics
44-year-old male presented with tortuous varicose veins and severe symptoms including swelling, pain, skin discoloration, and itching. His symptoms were worsened by his profession which required long hours on his feet.
Despite a previous GSV ablation and trying conservative therapies including compression stockings, leg elevation, and participation in an exercise program, the patient continued to experience lifestyle-limiting symptoms that prevented him from working and interrupted his sleep.
Patient assessment: CEAP class 3
- Bilateral GSV reflux with multiple incompetent truncal branches was confirmed with duplex ultrasound
- The diameter of the GSV above the knee in the left leg was 6.6mm with a reflux of 2.3 seconds and significant tortuosity
Treatment and results
After vein mapping, four separate treatment sessions were proposed to treat the extensive bilateral disease.
During the first treatment, the left GSV was punctured with a 23g butterfly needle infusion set using ultrasound guidance and then the leg was elevated.
5 cc’s of Varithena was used for the first treatment of the left GSV truncal branch. At the second visit 6 months later, the patient received 10cc’s of Varithena for treatment of the left distal GSV.
The patient was asked to dorsiflex their ankle to limit the drug’s movement into the perforating veins until spasm was confirmed with ultrasound in the treated vein.
Compression was applied to the leg with short stretch wraps from the distal foot to the groin and the patient ambulated for 10 minutes in the clinic.
After the second of four proposed treatments the patient has experienced a significant improvement in symptoms and has not experienced new symptoms.
Conclusion
Multiple visits were proposed to treat the patient's bilateral disease. The patient tolerated the first two procedures on the left leg without complications. The patient’s progress will be monitored as they continue with his proposed treatment program. He has been counseled on the importance of following up with subsequent appointments to complete treatment, even though his symptoms are feeling better.
He has been pleased with his results and was able to return to work to stand on his feet for long periods of time without symptoms.
Documentation

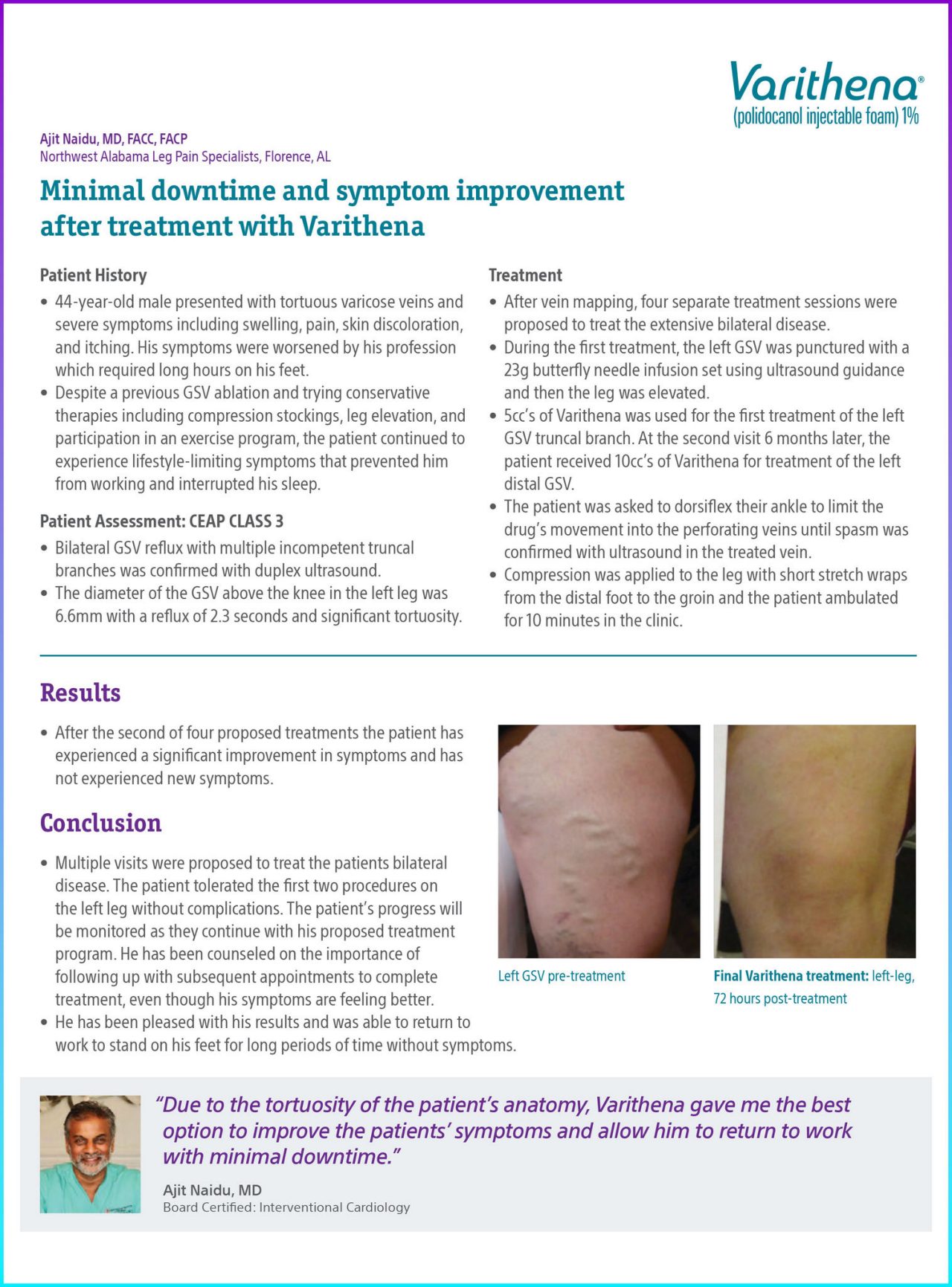
Figure 1. Left GSV pre-treatment.

Figure 2. Final Varithena treatment: Left-leg, 72 hours post-treatment.